Different Types of Steel
Steel is the most common metal in the world, making it a versatile material for construction, manufacturing, and many other applications. It is a ferrous alloy composed of approximately 99% iron and 1% carbon. The four types of steel are alloy steel, carbon steel, stainless steel, and tool steel — with stainless and carbon being the most used by volume.
Keep reading to learn about the differences between stainless steel vs. carbon steel.
Stainless Steel

Stainless steel is used throughout hundreds of applications in domestic, architectural, transport, medical, food and drink, and pharmaceutical industries. Its durability, strength, and corrosion resistance make it ideal for everything from surgical instruments to industrial piping.
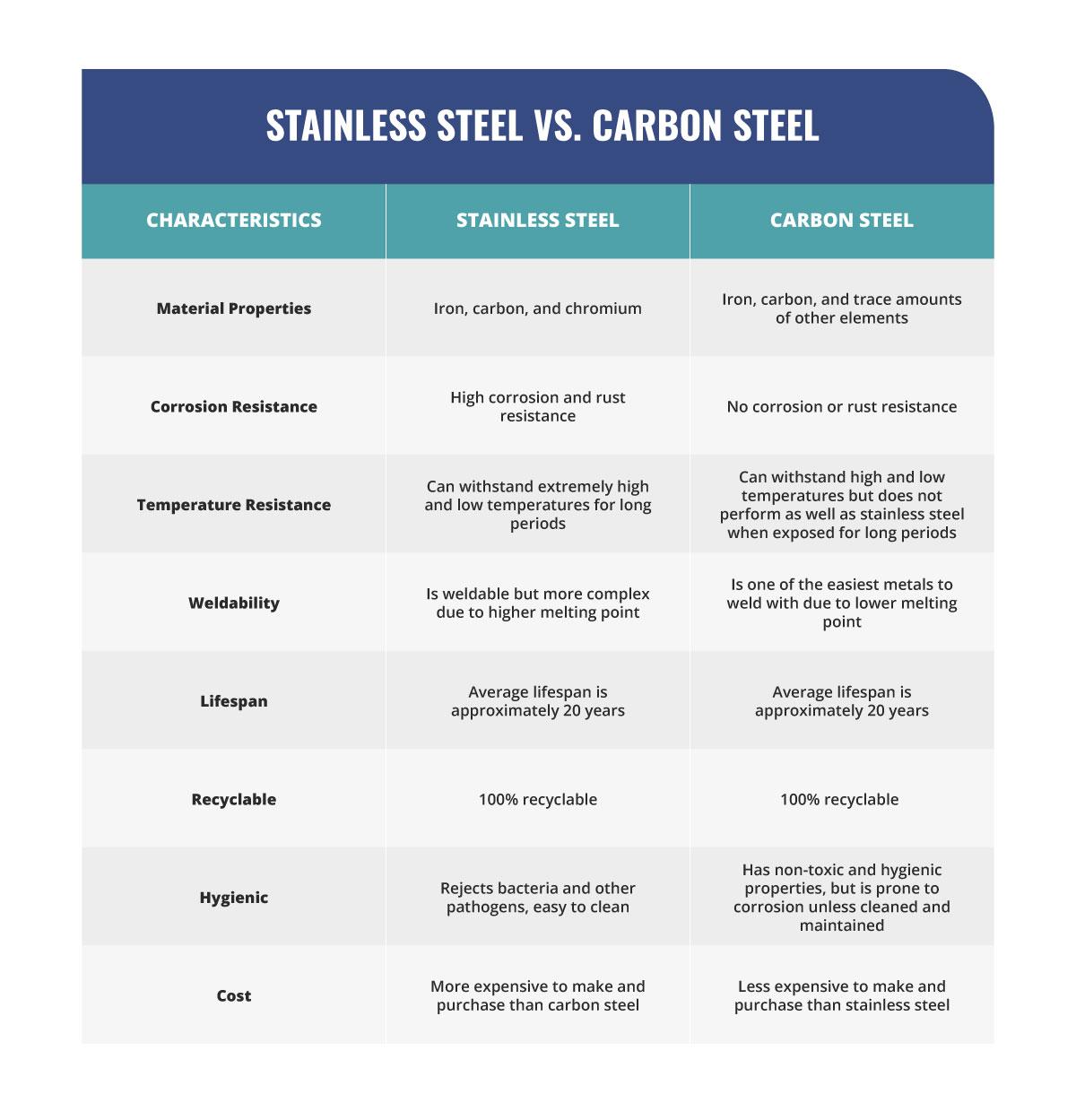
Stainless steel is a low-carbon steel alloy containing an average of 18% chromium and varying amounts of silicon and manganese. Chromium gives steel durability by hardening and increasing its corrosion resistance in high-heat or oxygenated environments. In some grades, nickel and molybdenum are also present to increase corrosion resistance further.
Stainless steel is divided into five primary categories:
-
Ferritic: Chromium-based with less than 0.10% carbon. Limited in use.
-
Austenitic: The most common type of stainless steel with the addition of nickel, manganese, and nitrogen to increase weldability and formability.
-
Martensitic: Similar to ferritic, but with a higher carbon concentration. It has high strength but lacks the corrosion resistance of austenitic steel.
-
Duplex: Approximately 50% ferritic and 50% austenitic. It’s known for its high strength and resistance but is fragile during welding.
-
Precipitation Hardening (PH): Comparable to austenitic steels given extremely high strength, with the additions of copper, niobium, and aluminum over an aging heat treatment.
Benefits of Stainless Steel
The main benefits of stainless steel include the following:
- Corrosion and rust resistance: When chromium is added to stainless steel during manufacturing, it combines with oxygen in the air to create a thin protective film over the metal, protecting it from rust and other corrosion.
- Temperature resistance: Certain types of stainless steel can resist scaling and can withstand extremely hot temperatures. Specific grades of stainless steel can also withstand long-term cryogenic temperatures.
- Tensile strength: All grades of stainless steel have extreme tensile strength. Both cold-hardened and heat-treated stainless are relatively lightweight despite their strength and durability. All grades have high shock resistance and can endure heavy loads.
- Long lifespan: Stainless steel is ideal for use in long-term applications where it is exposed to moisture or other corrosive substances, because of its corrosion and temperature resistance.
- Low maintenance: Stainless material will withstand the test of time with little-to-no maintenance required.
- Recyclable: Stainless steel is one of the rare materials that are 100% recyclable and can be used multiple times without sacrificing quality and strength.
- Versatile: The many grades and types of stainless steel make it useful in many applications. It can be rolled, forged, and cast into different sizes and welded, machined, or formed to create different shapes.
- Hygienic: Thanks to its chemical makeup, stainless steel naturally rejects the growth of bacteria and other pathogens. It’s also extremely easy to clean with a basic wipe-down and an all-purpose cleaner.
Uses of Stainless Steel

Most often, stainless steel is used for applications requiring steel’s unique properties and corrosion resistance. This alloy is milled into coils, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. Here are some examples of common stainless steel uses:
- Kitchen appliances: Stainless steel is commonly used to construct kitchen appliances such as refrigerators, ovens, and dishwashers.
- Sinks and countertops: Stainless steel is often used in the construction of sinks and countertops due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Food processing equipment: Stainless steel is widely used in the food industry for its corrosion resistance and hygienic properties. It is often used to construct food processing equipment, such as mixers and storage tanks.
- Medical equipment: Stainless steel is a popular choice for the construction of medical equipment due to its corrosion resistance and sterilization ability.
- Automotive parts: Stainless steel is used to construct various automotive parts, including exhaust systems and trim.
- Architectural and construction: Stainless steel is used in the construction of buildings and other structures, including handrails, doors, and window frames.
- Aerospace and defense: Stainless steel is used in constructing aircraft and other defense-related equipment due to its strength and durability.
- Chemical processing: Stainless steel is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for chemical processing.
Carbon Steel

Carbon steel, as its name suggests, is primarily made from iron and carbon with trace amounts of various other elements. It is cheap to manufacture yet strong enough to use in construction and manufacturing, making it the most popular of the four steel grades. As a result, carbon steel accounts for 90% of all steel production.
Most other types of steel contain small amounts (0.05% - 0.3%) of carbon, but carbon steel can contain anywhere up to 2.5% carbon. Types of carbon steel are broken down into three subgroups depending on the percentage of carbon material:
- Low carbon steel: Contains up to 0.3% carbon
- Medium carbon steel: Contains anywhere from 0.3% to 0.6% carbon
- High carbon steel: Contains more than 0.6% carbon
Benefits of Carbon Steel
The main benefits of carbon steel include the following:
- Durability: Carbon steel is strong, durable, and can withstand high stresses and loads from work impact. It’s commonly used in the construction of mechanical components and buildings.
- Affordability: Carbon steel is cheaper to manufacture and purchase than other steel forms.
- Recyclability: Carbon steel is also 100% recyclable and can be used multiple times without sacrificing quality and strength.
- Versatility: Carbon steel can be used in nearly every application where less expensive, durable materials are required. It can be welded, machined, or formed to create different shapes.
Uses of Carbon Steel

Stainless steel is frequently used whenever durability is needed at a more affordable price than other types of steel or when corrosion resistance is unnecessary. Often carbon steel will be manufactured or fabricated in mass quantities. Below are some common uses of carbon steel:
- Construction: Carbon steel is often used in the construction of buildings and other structures, such as bridges, due to its strength and durability.
- Automotive: Carbon steel is used in the construction of a variety of automotive parts, including engines, transmissions, and wheels.
- Industrial equipment: Carbon steel is used in the construction of a variety of industrial equipment, such as boilers, tanks, and pressure vessels.
- Machine parts: Carbon steel is often used in constructing machine parts, such as gears, bearings, and springs, due to its strength and durability.
- Piping: Carbon steel is commonly used in the construction of pipes and piping systems due to its strength and versatility.
- Cutting tools: Carbon steel is used in constructing cutting tools, such as knives and saws, due to its ability to hold a sharp edge.
- Defense: Carbon steel is used to construct various defense-related equipment, such as armor and weapons, due to its strength and durability.
Which Steel Should I Use?
Chromium gives stainless steel its corrosion-resistant properties, making it ideal for use in various applications exposed to moisture or other corrosive environments. On the other hand, carbon steel’s relatively high carbon content gives it strength and hardness, making it suitable for various applications requiring high stress and impact.
Using carbon or stainless steel will depend on your project’s specific requirements and factors, including material properties, corrosion and heat resistance, and costs.
Mead Metals Is Your Place for Stainless and Carbon Steel
Mead Metals is an ISO-certified metal service center and supplier of high-quality, low-volume metals. Our stainless and carbon steel products include:
Whether your project requires large or small quantities, we can accommodate without exorbitant lot charges. We also offer a variety of machining and delivery services with quoted lead times of up to 99.98% accuracy.

If you’re still unsure what type of steel you need for your project, our Steel Comparison Guide provides in-depth information on how different varieties stack up against one another. Download it for free today:




